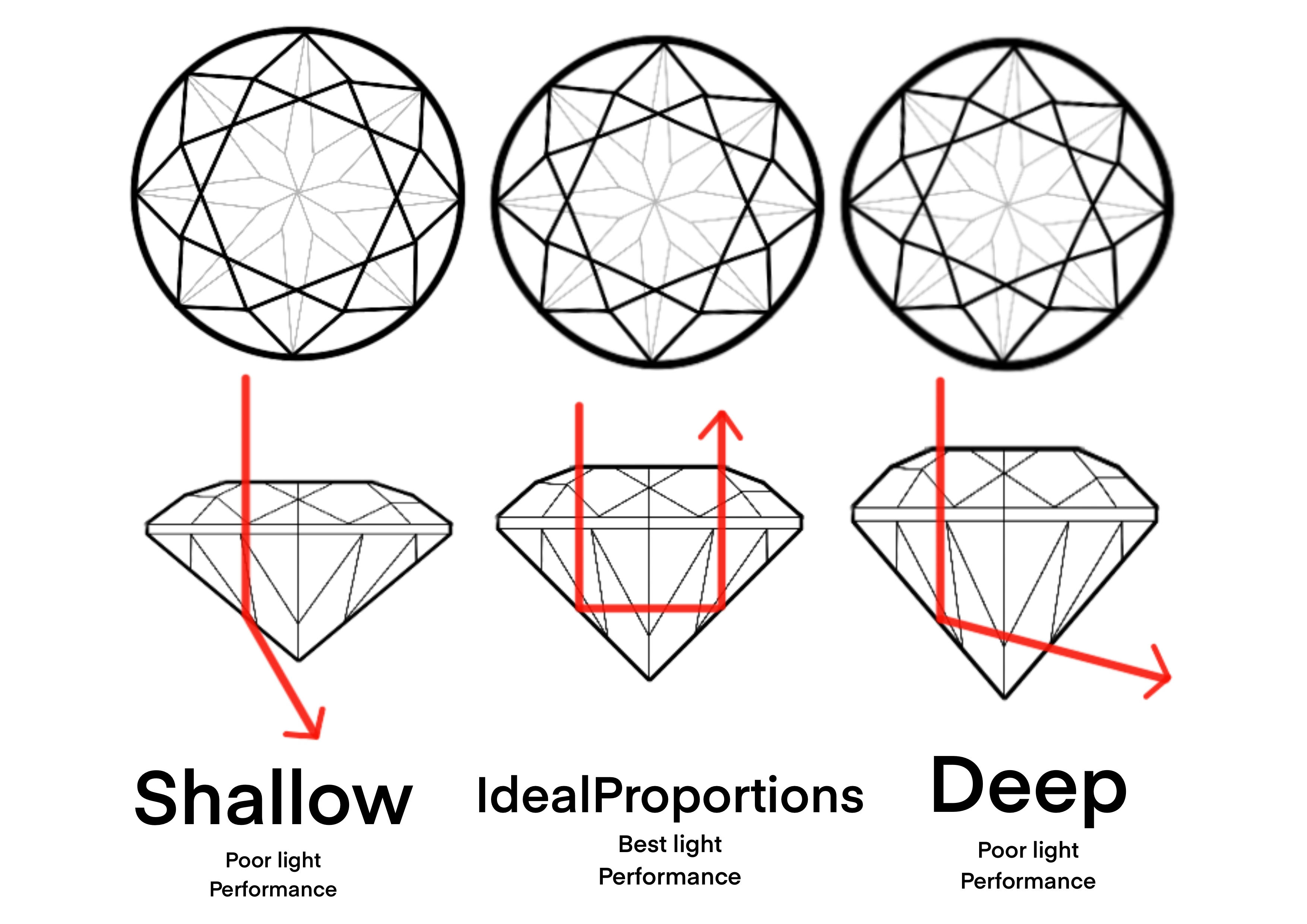
What is Cut?
This does not refer to the diamond's shape (e.g., round, oval), but rather to how well the diamond has been cut from its rough form. Factors include brightness (internal and external white light reflected), fire (the dispersion of light into the colours of the spectrum), and scintillation (the play of light and dark areas and the sparkle when a diamond is moved). Graded from Excellent to Poor, the quality of a diamond's cut affects its brilliance.
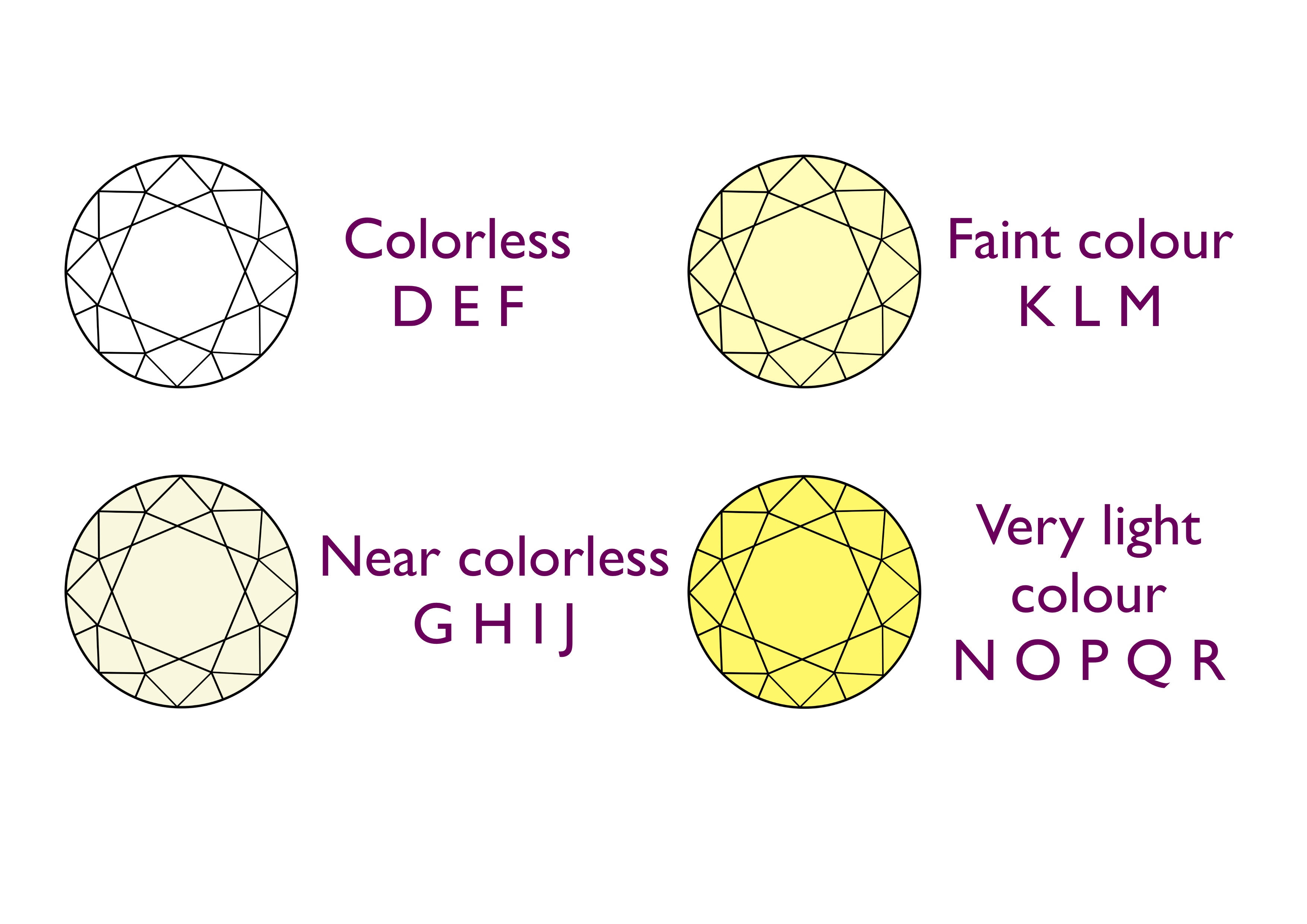
What is Color?
Diamonds are graded on a scale from D (colourless) to Z (light yellow or brown). Typically, the more colourless a diamond is, the more valuable it is. The difference between one grade and another can be very subtle, often invisible to the untrained eye but can make a significant difference in price.
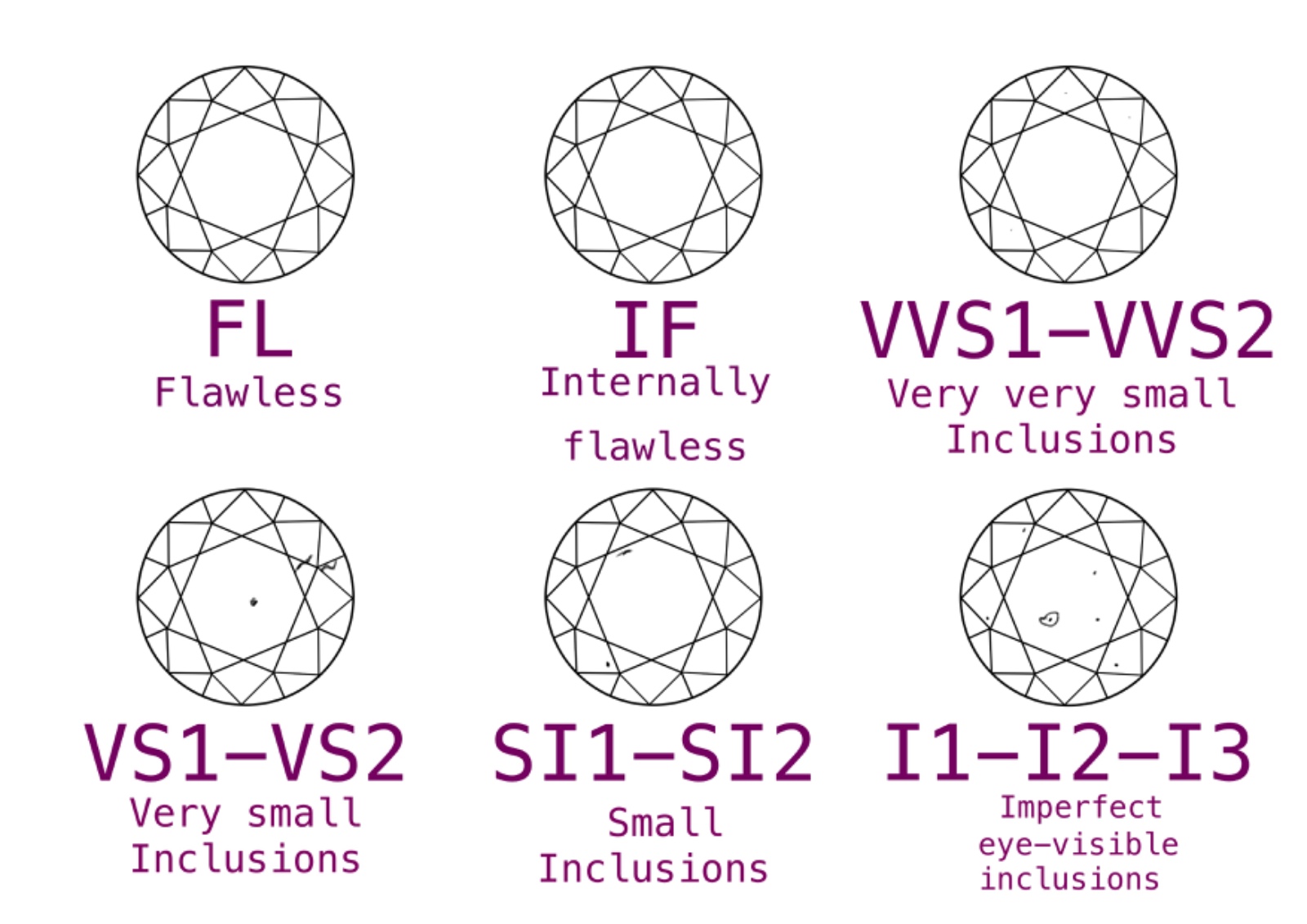
What is Clarity?
Refers to the presence of internal or external imperfections, known as inclusions and blemishes respectively. Scale ranges include Flawless (no inclusions or blemishes visible under 10x magnification) to Included (inclusions and/or blemishes visible to the naked eye). Many inclusions are microscopic and do not affect the beauty of the diamond to the naked eye.
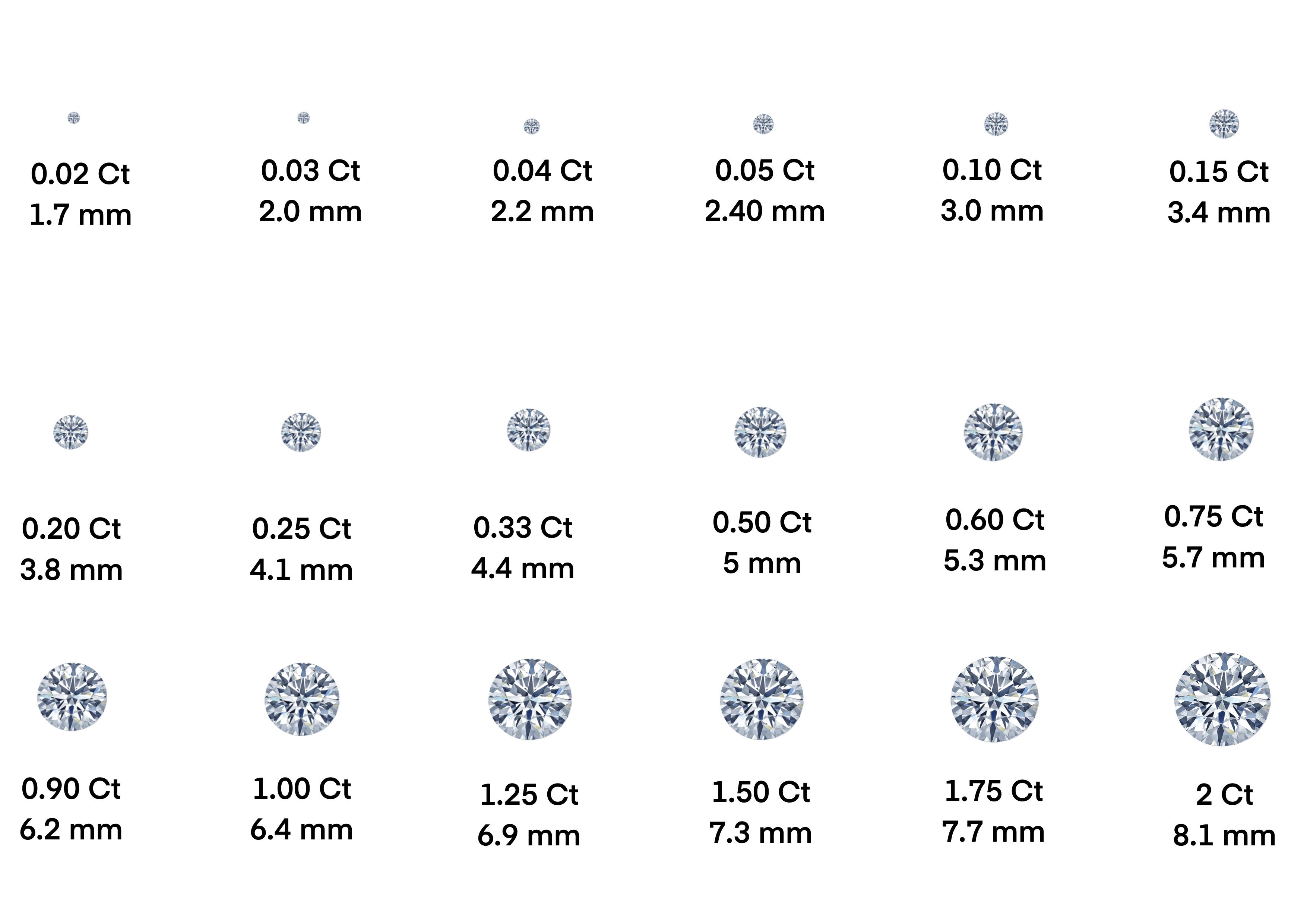
What is CARAT WEIGHT?
One carat is equivalent to 200 milligrams. A diamond's value rises with carat weight, given that larger diamonds are rarer. It's crucial to remember that a diamond's value isn't just determined by its carat weight. Two diamonds of equal carat weight can have very different values and prices depending on the other three Cs.